LEAN Tools
- 5S
Workplace organization - KANBAN
Material management - LEAN OFFICE
Optimization in the office - DESIGN THINKING
A way of thinking - LAYOUT
Internal logistics - SMED
Rapid changeover - SOP
Standardization of work - TPM
Total Productive Maintenance - TWI
Training Within Industry - KPI
Visual Management - VSM
Value Stream Mapping
Find out more from the experts
Talk to Lean Idea
+48 607 86 49 85
KANBAN
Production Flow Planning and Control System
KANBAN is a word of Japanese origin, consisting of two elements: KAN => card and BAN => signal. It is a production flow planning and control system.
Determination of machine capacity in terms of load and product variety
Analysis of changeover times
Determining the optimum production sequence
Reduce losses, gain an advantage
There are many methods and tools that serve the purpose of production process planning. The success of the company on the market and meeting the requirements of constant competitiveness depends on proper planning of what, when, and by whom should be implemented.
What is kanban?
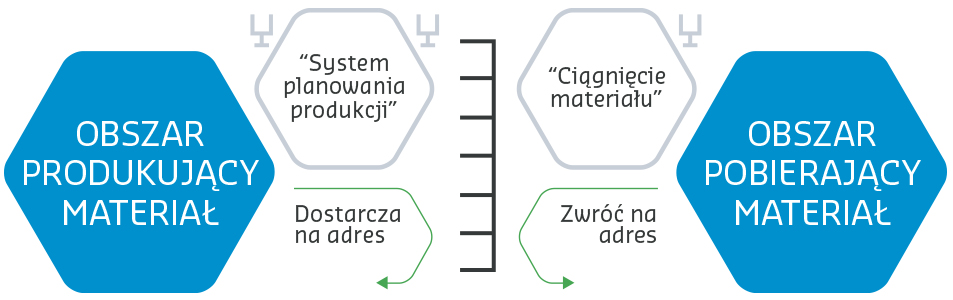
One of the methods used for production planning is Kanban, which informs about the moment when the product will be consumed by the process downstream. Kanban controls material movements, considering both time and quantity, depending on signals from the downstream process. Simply put, material production only occurs when a specific amount of it is consumed.
KANBAN functions
Pulling material – authorized material movement; What, when, how much, how to deliver, in what quantity, where to deliver from…
Production planning system – authorized material production; Quantity of products, packaging, required components, required machine/tool..
Kanban cards should contain at least the following information:
- material name
- article number
- place of collection
- place of transfer
- production stage
- number of pieces per container
- type of container
Benefits
Kanban is a continuous improvement tool that serves the enterprise in many ways:
- Production managers have the ability to avoid material overproduction between individual production processes
- It ensures transparency of material flow
- It contributes to reducing the production space to the necessary minimum
- It enables determination of the production capacity of machines in terms of their load and product variety
- It allows for the determination of the optimal production sequence.
We are there for you!





